When it comes to staying healthy and getting the medical care you need, having the right health insurance is essential. Health insurance provides financial protection against unexpected healthcare expenses, ensuring that you can get the care you need without worrying about how to pay for it.
There are many different types of health insurance plans available, each with its own set of benefits and drawbacks. In this article, we will explore some of the most common types of health insurance plans, including Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs), Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs), Point of Service (POS) plans, High Deductible Health Plans (HDHPs), Health Savings Accounts (HSAs), and other options.
By understanding the differences between these plans, you can make an informed decision about which type of health insurance plan is right for you and your family.
Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs)
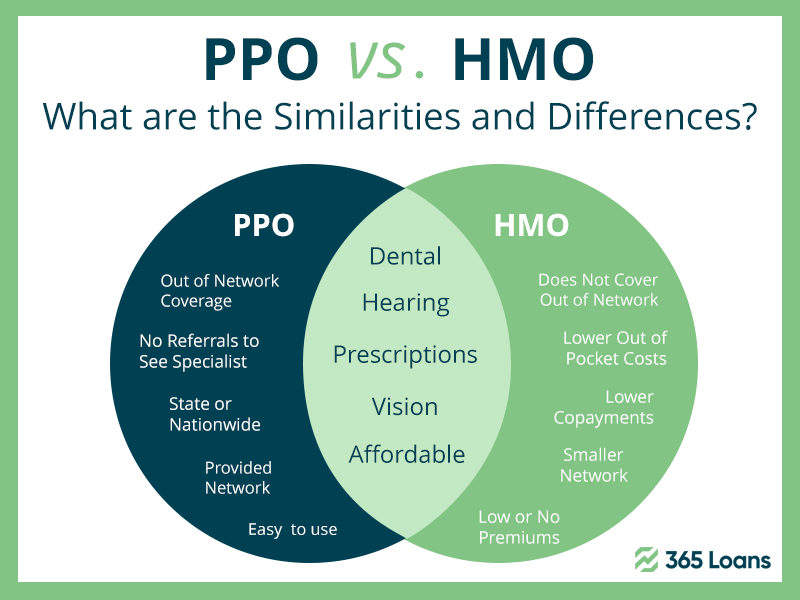
Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs) are a type of health insurance plan that operates by providing healthcare services through a network of healthcare providers. HMOs have lower costs and emphasize preventive care, but have limited provider networks and require referrals from a primary care physician for most medical services. An example scenario to illustrate HMO coverage could be a member of an HMO developing a persistent cough, visiting their PCP, being diagnosed with bronchitis, and being prescribed medication. If necessary, the PCP may refer the member to a specialist within the HMO’s network.
Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs)
A Preferred Provider Organization (PPO) is a type of health insurance plan that allows members to choose from a network of healthcare providers or seek medical care outside of the network. PPOs offer greater flexibility and larger provider networks compared to HMOs but can have higher costs and potential out-of-network charges. PPOs do not require members to choose a primary care physician or get referrals for specialists.
An example scenario of PPO coverage is that if you develop a persistent cough, you can choose to see any healthcare provider within or outside of the PPO’s network without a referral. However, you may face higher costs if you see an out-of-network provider, and may be responsible for additional charges if the provider charges more than the PPO’s approved rate.
Point of Service (POS) Plans
POS plans combine elements of HMOs and PPOs and require members to choose a primary care physician and obtain referrals to see specialists. They offer flexibility to see providers inside or outside the network, but out-of-network providers come with higher out-of-pocket costs. POS plans have lower costs for in-network providers compared to PPOs, but potential out-of-network charges are a main disadvantage.
An example scenario is seeking medical care for a persistent cough: seeing an in-network PCP incurs a copayment, while an out-of-network visit is more expensive. Seeing an in-network specialist with a referral is covered, but choosing an out-of-network specialist without a referral may result in full payment responsibility.
High Deductible Health Plans (HDHPs) and Health Savings Accounts (HSAs)
An HDHP is a type of health insurance plan with a higher deductible than traditional plans. It requires individuals to pay more out-of-pocket expenses before insurance coverage begins but typically has lower monthly premiums. HSAs are tax-advantaged savings accounts that individuals can use to pay for qualified medical expenses. HDHPs are often paired with HSAs, as individuals can use their HSA funds to pay for their higher out-of-pocket costs.
The main advantage of HDHPs and HSAs is their lower monthly premiums and tax benefits. However, the main disadvantage is their higher out-of-pocket costs, which can be difficult for those with chronic medical conditions. HDHPs may also offer limited coverage for certain services. Overall, HDHPs and HSAs can be a good option for healthy individuals looking to save on monthly premiums, but they may not be the best choice for those with chronic medical conditions or who require frequent medical care.
Other Health Insurance Options
In addition to HMOs, PPOs, POS plans, HDHPs, and HSAs, there are several other health insurance options available. Other health insurance options include short-term health insurance, catastrophic health insurance, employer-sponsored health insurance, Medicaid, and Medicare.
- Short-term health insurance provides coverage for a short period but may have limited coverage and exclude pre-existing conditions.
- Catastrophic health insurance covers major medical expenses but has higher deductibles and out-of-pocket maximums.
- Employer-sponsored health insurance varies in coverage, cost, and provider networks.
- Medicaid is a government program that provides health insurance to low-income individuals, while Medicare provides insurance to those who are 65 or older, have certain disabilities, or have end-stage renal disease.
Understanding these options can help individuals make informed decisions about their healthcare coverage.

Conclusion
In conclusion, this article has explored the differences between HMOs, PPOs, POS plans, HDHPs, HSAs, and other health insurance options. Each type of plan has its own advantages and disadvantages, and it is important for individuals to consider their healthcare needs and budget when selecting a plan. It’s also essential to remember that healthcare costs can quickly add up, making it crucial to have a plan that provides adequate coverage without breaking the bank. Additionally, selecting the right plan can help ensure that individuals receive the medical care.