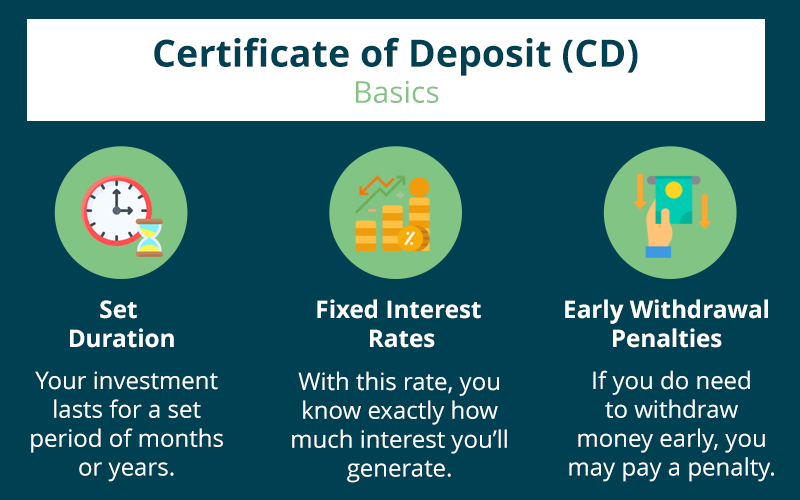
What is a Certificate of Deposit or CD?
An account that retains a fixed amount of money you deposit in a bank for a fixed period of time is known as a Certificate of Deposit or simply a CD. The tenure of a fixed period could be six months, a year, or five years, giving depositors flexibility in investment tenure. The bank in exchange for interest paid by the bank or credit union. When you decide to cash in your CD, your original investment amount plus interest is earned.
How a Certificate of Deposit (CD) works
As a customer, you deposit a set amount of money for a fixed term, available in months or years options. You are entitled to a higher interest rate than a regular savings or money market account. As per the agreement, the customer only agrees to withdraw the funds at the end of the term, and when the term is completed, the bank pays a higher interest rate.
Also, at the end of the term, the customer is given two options; either withdraw the funds or renew the CD for another term. CDs are low-risk investments insured by Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC).
Can you break a Certificate of Deposit (CD) early for a better rate
It depends as there are two conditions, and both are personal.
- Interest rates
The interest rate is guaranteed and fixed when you open the account for a Certificate of Deposit. Suppose the economy is not doing well, which may result in falling interest rates, but even that will not affect your CD. But there is a catch, what if interest rates go up? Then you might be tempted to break your Certificate of Deposit agreement with your bank and make a profitable move towards the higher interest-paying bank.
- Uncertain situation
Life is uncertain. So are the situations that one come across in life. In case of emergency or any unexpected expenses, one can go for breaking CDs early, which would be a sound choice compared to waiting for cash on investments.
Is there a penalty for the early withdrawal of a CD?
There is a penalty if you withdraw early, which varies from bank to bank. Also, fines are different for different tenures. For example, there is a higher penalty if your CD tenure is 5 years, and there is a lower penalty if your CD tenure is 3 months or 6 months.
There is one more downside to early withdrawal. Although your bank or credit union will take penalties from your earned interest, that does not mean your principal amount is safe. If you opt for an early CD break, and your accumulated interest is less than the penalty’s total amount, then your bank will take the difference in an amount from your principal investment.
Possibilities where you can break your CD early
Financial emergency
Uncertainty can knock on the door anytime. If you don’t have savings stored somewhere else or passive income, then breaking the CD might be the only option. Even if you are hit with a penalty, that would be lower than that interest on a personal loan or tax penalty if you borrow from an IRA. A minor penalty for getting your principal back is better than paying interest for a longer term.
Taking advantage of higher interest rates
Interest rates go up, and breaking from your previous CD is a lucrative option. In that case, you can compare the penalty and the next CDs interest rate. For example, if your current CD has six months maturity period left, you should calculate how much interest you will receive with the new CD for the next six months. If the interest rate on the new CD is higher than the penalty, you can easily choose to break with your previous CD.
Compare rates
When breaking a CD and looking for a new one, always look for a higher interest Certificate of Deposits (CDs). Different banks and credit unions offer different interest rates. Also, you should consider which bank charges a lower penalty for early withdrawal or if the bank waivers the penalty to keep your business.